HOW TO RANK IN GOOGLE?

With ever-changing algorithms and more than the so-called 200 ranking factors, ranking in Google today is not an easy task.
As per Singlegrain,
Google made approx 3000 changes in its search engine algorithm in 2018. It is more than eight times the updates made in 2009.
Wondering how to rank in Google?
Here’s a list of 13 actionable tips that can bring your site in ranking, and if done persistently, you can hit the #1 spot too!
Step 1 : Keyword Placement
After you have a list of keywords ready, the next step is to sprinkle them into your content.
Choose one main keyword that describes the overall topic of the page.
It should be your H1. After H1, use it again in the first 100 words (introduction) on your page.

Your secondary keyword should be your subheading (H2).
Google doesn’t restrict the number of keywords in the content. But where you place them matters.
Apart from the content, they should appear in your URL and title tag.

Also, evenly distribute your keywords throughout the article.

Make sure your keywords appear naturally and don’t break the flow while reading.
In addition to that:
Use emotions in your titles.
Various studies have found that emotional headlines = higher CTR.
But don’t go overboard with emotional words in your headlines.
In short, write compelling headlines that people will love to take action on.
Step 2 : LSI KEYWORDS
Back in the day, Google used to understand the topic of your content only based on keywords.
But today, Google ranks a page around topics, not keywords.
For example:

Google will infer that, ok, all the keywords are around running shoes. So, the overall topic of the page is “running shoes.”
These are called LSI keywords.
You can quickly find these keywords from the LSI keywords Generator tool:

Another tool that you can use is LSIGraph. I typed in ‘plants’ and these are the LSI keywords:

Step 3 : Search Intent
Google is determined to show results that match most with users’ queries.
A simple way to check this is SERP.
Go through the pages that already rank on your keyword and produce similar content.
For example,
I was thinking of clubbing the steps for this blog under on-page SEO, off-page SEO, technical SEO, and user experience.
But I found out that the pages that are already ranking speak differently. They have simply written it in steps format.
So, I, too, wrote it similarly.
Additionally, Semrush has introduced a new feature that allows you to know the search intent.

Step 4 : Content
According to Google, content is one of the top three ranking factors.
Here are a few quick tips:
- Use keywords but don’t over-optimize.
- Use heading tags to make it skimmable and properly structured.
- Write lengthy content.

But it is no hard and fast rule.
If the pages that rank on your keyword are 600 words, don’t go big and write 2000!
But in any case, your content should be complete in itself.
- Use simple language, short sentences, bold the bullet points, use italic while quoting someone. It will make your content more scannable.
- Your content should be grammatically correct. I use the Grammarly tool before uploading any content on my site, and it just adds wonders to it.
- Use multimedia (images, charts, graphs). You can download high-quality images from Unsplash. You should always consider compressing them before uploading. The Squoosh tool compresses images without deteriorating their quality.

- Mention other sources, like data from original research on your topic. Who better to be quoted than Google while writing for SEO!
- Write less theory and more actionable tips.
Step 5 : Avoid duplicate content
Duplicate content is when similar or precisely identical content appears on multiple URLs. These URLs can be of the same website or on different sites.
Let’s say you have a page that shares the same content with three other pages. In this case, Google can’t decide which page to be ranked.
It will keep the original page from ranking.
Also, a lot of your crawl budget can get wasted crawling such pages.
Therefore, crawlers might not be able to visit pages that could rank.
It creates a possibility for the original page not to rank as Google can’t decide which page to rank.
Here are a few quick steps you can take:
- Use 301 redirects: it is the permanent redirect to send users to a particular URL. So, if you have a couple of pages that share the same content, redirect them to the original one.
- Use the rel = canonical tag: The tag tells Google which page is important to you. Place the canonical tag in the page’s head section that you want to consider out of the set of duplicate pages.
- Minimize similar content: For instance, if you are a mental health blogger and have two separate blogs on anxiety and stress, but they both share very similar content, you can club them together.
- Use the “noindex” tag: add the “noindex, follow” tag to each page you don’t want Google to index. As per Google, it should not be restricted from crawling a page that has duplicate content. So using this tag, they can still crawl it but won’t index it.
- Every page should have unique meta tags, URLs, and heading tags.
Use the Siteliner tool to detect duplicate pages on your site.
I checked it for my site too.

Step 6 : Anchor text
Google determines link relevancy by two factors:
- Content on the target page.
- Anchor text that is used to link that page.
Google uses anchor text to understand the context of the page linked.
Here’s how you should write anchor text:
- Anchor text should be relevant to the destination page.
- They should be short and descriptive.
- Avoid using generic anchor texts.
- They should contain your target keyword but don’t over-optimize.
- Pay attention to the content around the anchor text. It should be in sync with the anchor text.
- Use different anchor texts for other pages.
Let’s say you have two pages; one talks about feature phones and the other about smartphones. But you linked them on different pages using the exact anchor text “phones,” It will tell Google that these pages talk the same thing.
Step 7 : Internal Linking
The pages on your site should be well connected.
It will help crawlers to navigate your website quickly and index more pages.
Also, when you create a new page, it has zero authority.
Internal linking can help pass some authority to your newly created page.
That will help Google find your page faster as well.
You can take the help of a tool here.
Go to Semrush and find pages with high authority on your site. Use these pages to link to your fresh content or any page that you wish to rank.
Ninjaoutreach conducted an SEO campaign in which they found out that internal linking helped them boost their organic traffic by 40%.
Anchor text plays a part here too!
As per Google, anchor texts are an essential part of internal linking too:

Try putting any link at the beginning of the page, as not everybody will reach the last fold.
For example:
I recommend you pass my SEO Quiz to test your SEO knowledge.
Here, SEO Quiz highlighted in blue is an anchor text and creates an internal link – because when you click the link, it takes you to another page on my website.
Step 8 : Mobile friendliness
Google is mobile-first index.
It means your site should be even faster on mobiles as compared to other devices.
As per a report by Statista, in the US, mobile devices contributed to 61% of organic search visits in the second quarter of 2021.
To check the mobile speed, you can run your Mobile friendly test by Google:

Step 9 : Speed test
Google doesn’t want to show slow results to its users.
Page speed is an important technical factor to be looked after.
In a study by Pingdom
page load time directly impacts the bounce rate. It states that the average bounce rate for a page loading within 2 seconds is 9%.
To check your page speed, use Google’s Page Speed Insight tool. I checked it for my site and here is the result for desktop:

Here is the result on mobile:

Additionally, you can also use the Pingdom tool:

Here are some of the best practices for making your rocket fast:
- Keep the codes clean.
Check your hosting: Shared hosting is ok if you have a small website. But as your site expands, switch to a dedicated server. - Check your hosting: Shared hosting is ok if you have a small website. But as your site expands, switch to a dedicated server.
- Compress your images.
Step 10 : Crawling
Crawling is the very first step in ranking.
Each site has its crawl rate.
Let us understand why it is essential from an SEO standpoint.
Every new page you add to your site can crawl fast. So, the number of pages getting crawled on your overall site will increase.
Any change that you make to your site will be tracked fast.
You can check it on the google search console.
Go to settings > crawl stats.
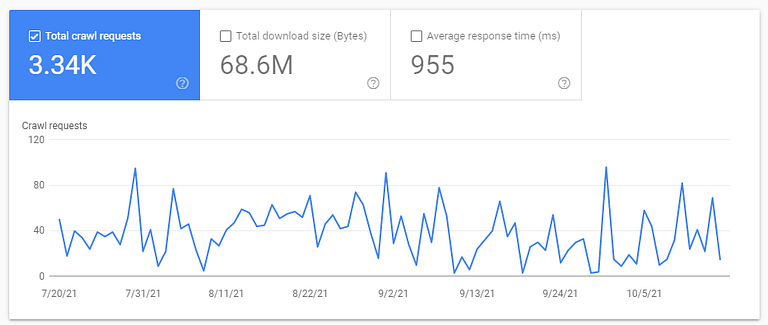
Here are a few quick tips to increase your crawl rate:
- As crawlers follow the link path, you should have good internal linking for your site.
- Avoid orphan pages. Link them to other pages on site.
- Do not use duplicate content. It will waste your crawling budget.
- Keep updating your content. Crawlers like to visit pages with new content.
- Try to avoid redirects (especially in the loop). A crawler might drop off your site.
- Have a good site structure.
Step 11 : Site structure
Create a hierarchical structure: homepage > category page > product page.
Each page should be linked by at least one of the pages on your site.
It will help crawlers navigate through your site quickly.
It is even more critical for big websites with lots of web pages.
Site structure helps in grouping similar pages on your site. It is called topically grouped content.
For example, if you are a life wear brand, you can categorize them as dresses, bottoms, accessories, loungewear, etc.
This way, Google will easily understand your site. Also, it will be quick for users to find various pages.
A good site structure can tell Google which content is precious to you.
These are called pillar pages. You can link all other pages on your site with them.
Step 12 : Backlinks
More the number of backlinks, more the search traffic on your site:

It will also help in boosting up your ranking in Google.
Also, getting more and more backlinks opens more paths for crawlers and readers to enter your site.
Therefore, increasing your referral traffic and chances of getting indexed.
TIP: By publishing original research, you can become an excellent link source as your content will have lots of data, stats, and figures.
BEST PRACTICES:
Broken Link Building:
It is when you replace broken links on another site with your link with similar content.
Whenever you come across any dead URL, copy-paste it in a tool like Semrush.
Go to backlink analytics > backlinks. It will generate a list of all URLs linking to this page.
Produce great content on that same topic and reach out to the author of these pages via emails.
It’s a win-win situation. Site owners will get to replace a broken link on their site, and you will get a mention too.
Here’s one email that I wrote. I also included the screenshot as a proof.

Guest Blogging:
Guest blogging is when you do blogging on others’ websites.
The website will give your mention as the editor or author there.
For instance, If you write a blog for site A, people on-site A would be your audience. If this audience likes your blog, they will directly visit your site and become your direct audience.
This way, you can increase traffic on your site.
It will also help you build intern personal relationships with people from your industry.
Step 13 : Improve Your Website's SEO Performance
Organic CTR:

As you can see, the steep fall is right from position 1 to position two on SERP.
An increase in the number of clicks = increase in traffic.
With more traffic on your page, Google will infer that it is popular among users, consequently boosting its ranking.
You can check your organic CTR in Google Analytics.
Go to the Performance tab on the left-hand side:

Here are quick tips to boost the CTR for your site:
- Titles: your title and descriptions should be unique for each page. Use emotional titles as they are more appealing.
Use your target keyword but don’t overdo it. Also, mention the fantastic point about your page, could be a complete guide, embedded video, all in one listicle, etc.
- Description: Give a brief intro, features, and how readers will be benefited from your content. Include a CTA, reflect your brand tone.
- Have short URLs:

As you can see, shorter URLs tend to rank better. Keep them around 50-60 characters. Try including your target keyword in the URL.
Rich Schema: these are an excellent way to enrich your SERP listing. Rich schemas provide more information than regular snippets.
You can use JSON-LD to implement the structured data on the web. It gives various data types like rating, timings, dates, venues, etc.

You can test the structured data on Google’s Rich Results Test.

Bounce Rate:
Bounce rate is an indirect ranking factor.
If your page has a low bounce rate, it means people are staying on your site and going from one page to another.
When Google finds that visitors like a page, it will naturally boost up its ranking.
To check the bounce rate, go to Google Analytics:
Behavior > Site content > All pages

Here are the quick tips to reduce your bounce rate:
- Make your content skimmable.
- Use bullet points and avoid bulky paragraphs.
- Avoid popups/interstitials.
- Improve your site speed.
- Make your site structure even. The parent page should not be more than three clicks away from the product page.
- Have a consistent internal linking throughout your site.
BONUS:
Keep a regular check of your site’s performance in the search console.
Look out for the keywords that are getting impressions but no clicks. These are the keywords that Google thinks are relevant to your site.
As these keywords are coming from Google itself, it’s a great idea to create new articles around them.
You can also add them to an existing article and improve it.
One thing you should avoid is keyword cannibalization!
It is when you rank for keywords with more than one URL on your site. It will make these pages compete with each other for ranking.
It causes Google to lower the quality and authority of your pages.
Yet again, search intent plays a significant role here! These keywords may be different, but the search intent or user’s query can be the same.
It is more common on websites with lots of articles.

